Background
This paper describes a model built by PM Power Consulting mapping Stakeholder outcomes to Agile enablers. The primary source for building the model was PM Power’s book, The Five Tantras of Enterprise Agility. Further inputs came from later inferences of PM Power’s consultants and coaches working with many large and medium organisations while guiding them in their Agile Transformation journey.
The model was built by the following PM Power consultants: S. Srinivasan, S. Sivakumar, S. Vasudev, Dr K. Prasad and Paramu Kurumathur over a period of six months, under the mentorship of J. Veeraraaghavan.
Introduction
We look at three key stakeholders critical to the success of any organisation:
- Customers,
- Shareholders and
- Associates.
For each stakeholder we define a set of high level outcomes desired by the stakeholder. The success of each of these outcomes is predicated on the success of a set of indicators that are closely associated with the outcomes. The success of each of these indicators is influenced by the correct implementation and performance of a set of enablers (practices) that ensure the Agility of the enterprise. And, at the end of the chain, each enabler will have a set of actions to be performed to “enable” the enabler.
While the outcomes and associated indicators will serve as lagging indicators of the performance of an organisation with respect to the stakeholder, the associated enablers and the success of their implementations, will serve as leading indicators.
The Stakeholders
As mentioned before, the model looks at three stakeholders that have the most important roles in the success of an organisation.
Customer: The importance of the customer in the success of an organisation needs no elaboration. Customers drive revenues. Without them, the organisation cannot and need not exist.
Shareholder: Shareholders are the owners of the organization. They dictate the growth and investment patterns of the organization. In our model, the shareholder may be represented by top management executives acting on their behalf. The CEO, the CFO, the VP of Corporate affairs: these are some of the management types who represent the shareholder’s interest in the organization.
Associate: Associates are the backbone of the organization. They provide the services needed to create the organization’s products which are then consumed by the customer.
We will now look at the outcomes desired by each of these stakeholders as defined in PM Power’s model.
Outcomes
Outcome measurements and their associated indicators are lagging indicators that show how the organization has been performing in hindsight.
The following table lists the key outcomes of the three shareholders:
| Stakeholder | Outcome | Summary |
|
Customer
|
Continuous Value | In an environment that is continuously and rapidly changing, providing features and the right experience as and when required, with the required innovation. |
| Customer Empathy | Understanding the implicit and explicit needs and the underlying feelings of customers, by viewing things from their perspective | |
| Customer Relationship | Customers having a consistent and good experience and impression whenever they interact with the organization, including getting ideas on innovation and beating competition | |
|
Shareholder
|
Getting work done | The organization delivers to the business vision and expectations, operating autonomously while addressing all risks. |
| Healthy Culture | The organization provides transparency in its workings and takes ownership of outcomes. | |
| Shaping the future | The organization innovates and stays relevant for the future | |
|
Associate
|
Enriching Job | Associates are able to add value to themselves |
| Energizing Work Environment | Associates feel a sense of belonging in the organisation | |
| Building my career | Associates see a future for themselves in the organisation |
Outcome Indicators
The success of each of these outcomes above is predicated on the success of a set of indicators that are closely associated with the outcomes. We list below the indicators associated with each outcome mentioned above.
| Stakeholder | Outcome | Outcome Indicators | Summary |
|
Customer
|
Continuous Value
|
Timeliness | The organization provides features as and when required |
| Innovative Ideas | The organization incorporates innovative ideas for features. | ||
| Implicit Requirement | The provided features meet requirements that were not explicit. | ||
| User Experience | The features provide the right user experience. | ||
|
Customer Empathy
|
Listening | The organization listens to the customer | |
| Evolving Needs | The organization is empathetic to the customer’s evolving needs. | ||
| Responsive | The organization is responsive | ||
| Easy to work with | The organization is easy to deal with | ||
|
Customer Relationship
|
Innovation | The organization helps in innovation. | |
| Proactive | The organization proactively suggests solutions and technologies to help customer | ||
| In tune with Competition | The organization helps customers understand their competitive landscape. | ||
|
Shareholder
|
Getting work done
|
Vision/ Purpose Aligned | The organization operates to a higher order vision |
| Execution | The organization operates autonomously in the given environment to meet goals. | ||
| De-risked growth | The organization exploits growth opportunities even as risks are addressed. | ||
|
Healthy Culture
|
Ownership | The organization takes ownership for outcome(s) | |
| Collaboration | The organization operates in harmony with the rest of the organization. | ||
| Transparency | The organization provides adequate visibility to the state of affairs | ||
| Responsive | The organization acts on the inputs/ corrective actions provided by the board | ||
|
Shaping the future
|
Adequate Innovation | The organization is innovating. | |
| Building Capability | The organization is building the capability to stay relevant for the future | ||
|
Associate
|
Enriching Job
|
Experience helping Performance | Associates are enabled to exploit their experience. |
| Feeling Valued | Associates are valued for their contribution. | ||
| Get Recognition | Associates are recognised for their contribution. | ||
|
Energizing Work Environment
|
Conducive Team Environment | Team environments are conducive for high performance | |
| Aligned with Purpose | Associates feel connected with the organization’s purpose | ||
| Aligned with Values | Associates are aligned with the organizational values | ||
| Meritocracy | Associates feel merit is valued | ||
| Equitable practices | There’s equity in the organization (practices impacting people) | ||
|
Building my career
|
Sense of Achievement | Associates are nurtured for sustained accomplishment | |
| See a Future | Associates are enabled to stay relevant in the marketplace. | ||
| Realize potential | The organization actively helps their associates to realize their potential. | ||
| Overcome weakness | The organization helps their associates overcome their weaknesses. |
Enablers associated with the outcome indicators
As discussed before, the success of each of these outcome indicators (and therefore outcomes) are predicated on the successful implementation of a set of enablers that contribute to it. The enablers are categorised into groups that make them easy to implement together. It should be noted that some of the enablers could be ‘negative’; that is, they are to be ‘negatively’ enabled (or completely discouraged).
The enabler categories and the associated enablers are listed below.
| Enabler Category | Enabler | Enabler Type d: doing agile b: being agile c: capacity / capability item |
Summary |
|
Collaboration
|
Leaders Collaborate | d | Organization leaders “walk the talk” on collaboration |
| Collaborating Outside | d | Associates collaborate effectively beyond their team(s). | |
| Collaborating Within | d | Associates collaborate effectively within their tea(s) | |
|
Customer Interaction
|
Active Customer Involvement | d | Customers take an active part in implementation of products and features |
| Customer Feedback Acted | d | The organization gets back to the customer on actions that are taken based on customer input | |
| Effective Customer Interface | d | The organization interfaces effectively with their customers. | |
| Progress Visibility | d | The organization makes their work progress visible to customers. | |
|
Efficiency and Effectiveness
|
Fair share contribution | d | Each associate contributes a fair share to their team’s work. |
| Actively reduce waste | b | Team(s) actively reduce “waste” and inefficiencies | |
| Organized for Outcomes | b | Team(s) organise themselves to provide the best outcomes for their customers. | |
| Utilize Capability | d | Team(s) have an adaptive approach to deliver continuous value to the customer. | |
| Flexible in Roles | d | Associates do not restrict ourselves to defined roles in their teams | |
|
Enabling the current
|
Good Rewards & Recognition | d | Each associate is happy with the implementation of the organization’s reward and recognition schemes. |
| Motivated | b | Each associate is motivated to make a difference. | |
| Invest in New Skills | c | Each associate invests their time in acquiring new skills. | |
| Personal goals aligned | d | Each associate understands the connection between team goals and their personal goals. | |
| Sensing Leaders | b | Leaders sense the team’s unexpressed needs for guidance. | |
| Agile outcomes clear | d | The organization is clear about the outcomes expected from Agile adoption. | |
| Continuity in team | c | There’s adequate continuity of members in teams | |
| Building interpersonal skills | c | Associates are enabled to build their interpersonal skills | |
| Cross-skilling encouraged | c | The organization encourages cross-skilling of their people. | |
| Full-stack capacity | c | The organization has adequate capacity of full-stack engineers. | |
| Required Capability | c | The organization has the required capability (tools, environment, skills) to deliver continuous customer value | |
| Sustained product investment | c | The organization makes appropriate investments in their products on a sustained basis. | |
|
Holistic Understanding
|
Fair-share Interesting Work | d | Each associate is able to choose a fair share of interesting work. |
| Balancing Urgent & Important | b | The work environment nurtures a balance between ‘what is important’ and ‘what is urgent’. | |
| Listening to market-space | d | The organization has an ear to the ground on what’s happening in the market space | |
| Vision Internalized | b | The organization has internalized its vision | |
| Market changes mapped | d | The organization maps the developments in the market with the customer’s business challenges/ opportunities | |
| Understand Customers’ ecosystem | d | The organization regularly factors the needs of the ecosystem their customers operate in. | |
|
Learning Culture/ Practices
|
Active Common interest groups | c | The environment fosters informal common interest groups |
| Continuously adapting Agile | d | The organization’s implementation of Agile is based on continuously adapting from their learning. | |
| Sustained practice improvement | d | Team(s) improve work practices on a sustained basis | |
| Adapting to Changes | d | Team(s) adapt well to changes (external and internal) | |
| Balancing Experiments and Execution | b | Associates are encouraged to balance between planned work and experimentation. | |
| Learning Environment fostered | d | The environment promotes willingness to learn from anyone. | |
| Learning from Failures | b | The organization fosters open discussion of failures to learn from them | |
| Sharing our Learning | d | The organization has effective mechanisms for sharing their learning | |
| Regularly Abstract experiences | d | The organization regularly abstracts their own experience in their customer engagements | |
|
Measurement/ Feedback
|
Fair Compensation | d | Associate compensation is commensurate with their contribution. |
| Contribution drives growth | d | Associate growth is primarily dependent on their contribution. | |
| Outcome “over” Output | d | Measurements focus on outcome rather than output | |
| Measure Customer Value | d | Team(s) measure if the customer is getting the required value. | |
| Sustained Feedback Practice | d | The organization has a sustained practice of giving/ receiving feedback. | |
| Sense Customer Experience | d | The organization regularly senses the customer’s experience with them | |
|
Organizational Values
|
Mutual Trust | b | In teams, there is mutual trust and respect |
| Conducive to Curiosity | b | The environment is conducive for curious minds. | |
| Leaders back us | b | Leaders back teams when decision/ execution goes wrong. | |
| Facilitative leaders | b | Leadership style is facilitative | |
| Remedying under-performance | b | The organization proactively acts to remedy under-performance. | |
| Right-level decision making | b | The organization promotes decision making at the appropriate levels. | |
| Openness and Transparency | b | The organization promotes openness and transparency. | |
| Empowered to handle customer | b | Associates are empowered to deal effectively with customer needs | |
| No Blame culture | b | Associates desist from blaming others for their failures. | |
| Right Work-Life balance | b | Associates have the right work-life balance | |
| Mutually accountable | b | Associates hold themselves accountable to their team norms. | |
| Failure is personal | b | Associates look for personal accountability for failure of an initiative | |
| Accountable for Customer outcomes | b | The organization takes accountability for customer outcomes | |
| Diverse perspectives for decision | b | The organization takes into account divergent perspectives from stakeholders in their decision making. | |
| Value Teamwork | b | The organization values team work over individual brilliance. | |
|
Preparing for the future
|
Leaders encourage Discovery | d | Leaders ask open-ended questions that enable the team to discover the way forward. |
| Investing for a possibility | c | The organization invests in capabilities that could be potentially useful in the future | |
| Foster risk-taking | d | The work environment fosters risk taking. | |
| Up to date on Technologies | c | Associates keep themselves abreast with the current development in technology space | |
| Risk capital for Innovation | c | The organization provides adequate risk capital for product innovation. | |
|
Understanding Customer
|
Holistic understanding of Customer | b | The organization promotes holistic understanding of the customer’s context |
| Understand end-user scenarios | d | Team(s) actively use actual end-use scenarios in their implementation. | |
| Aligned with customer business | d | The organization is aligned with their customers business needs | |
| Understand Customer Needs | d | The organization understands the customer’s business challenges/ opportunities | |
| Understand Customer environment | d | The organization understands the customer’s technology environment | |
|
Work Practices/ Team Practices
|
Understand spirit of practices | b | Associates understand the rationale underlying their work practices. |
| Empowered on “how” | d | Leaders do not direct teams on how to do their work | |
| Customer Value focused process | d | Processes maintain focus on customer value | |
| Situational leadership | b | Team members take the lead as the situation demands. | |
| Deliver Chunks of Value | d | Team(s) deliver chunks of value, as opposed to, chunks of work. | |
| Manage temporary unavailability | c | Teams are able to perform their work even when key players are temporarily unavailable. | |
| Managed – Just Right | d | The organization is neither under-managed nor over-managed. | |
| Commit to Team decisions | b | The organization commits to decisions as a team in the face of disagreements. | |
| Work with Ambiguity | d | The organization continues to progress even with limited visibility on the needs/ outcome if the occasion demands. | |
| Accessible Leaders | d | Teams have the required access to higher levels of management | |
| Resolve Team conflicts | b | The organization resolves its team conflicts without affecting personal relationships. | |
| Full capability not prerequisite | d | The organisation starts its work even as they invest in building the required level of capability.. | |
| Delegation expectations understood | d | When decisions are delegated everyone understands what’s expected |
These enablers are mapped on to the various indicators, noting whether they influence the indicator at a high level (H) or a medium level (M).
For example,
- the indicator Get Recognition of
- the outcome Enriching Job of
- the stakeholder Associate
is mapped to the following five enablers:
- Good Rewards and Recognition (H),
- Sharing our Learning (H),
- Fair Compensation (H),
- Contribution Drives Growth (M) and
- Sustained Feedback Practice (M).
This means that the proper implementation of these enablers ensures that the associated indicator shows good results. Things to note here are: 1. An enabler will be associated with many indicators at (maybe) different levels. 2.The success of an outcome is predicated on the success of various indicators associated with it.
Each outcome indicator has a different number of enablers associated with it. Some have up to 30 enablers associated with it. It will take too much space to list all the indicator-enabler mappings.
Using the model
The model can be used to assess the success of the outcomes and indicators and also the implementation success of each of the enablers associated with them. These measurements can then be used to take actions to improve the enabler implementation and thus the success of the indicators and outcomes.
PM Power implementation of the model
PM Power has implemented an assessment engine based on the model above. Assessment of each of the outcomes, indicators and enablers is based on surveys conducted among the various stakeholders. Sets of people representing the three stakeholders are surveyed with questions representing each of the outcomes, indicators and enablers. The survey seeks responses to each of the questions indicating how successful (on a scale of 1 to 10) each item is. The following table gives a mapping of which stakeholder is asked which sets of questions:
| Survey Questions | Customer | Shareholder | Associate |
| (All Questions Scale 1..10) | |||
| Customer Outcomes (3) | Y | ||
| Customer Outcome Indicators (11) | Y | Y | Y |
| Shareholder Outcomes (3) | Y | ||
| Shareholder Outcome Indicators (9) | Y | Y | |
| Associate Outcomes (3) | Y | ||
| Associate Outcome Indicators (12) | Y | Y | |
| Outcome Enablers (83) | Y |
Perception gaps
The table shows that Customer outcome questions are asked only to customer representatives, whereas customer outcome indicator questions are asked to all three stakeholders. The reason why other stakeholders are asked customer questions is so that any perception gaps can be identified and acted on. It is important to look at these gaps and ensure that there is convergence in the understanding of the various stakeholders. Any effective action can be taken only after this convergence has been reached.
The enabler questions are asked only to the associates, since these are the people implementing these enablers. These outputs can be used by the organization to assess how well they are doing and set in place necessary corrective actions to improve the outcomes.
We said before that some of the enablers could be ‘negative’; that is, they are to be ‘negatively’ enabled (or completely discouraged). These negative effects would have been taken care of in the scoring, by adjusting it based on whether it is negative.
Some sample outputs from the engine are:
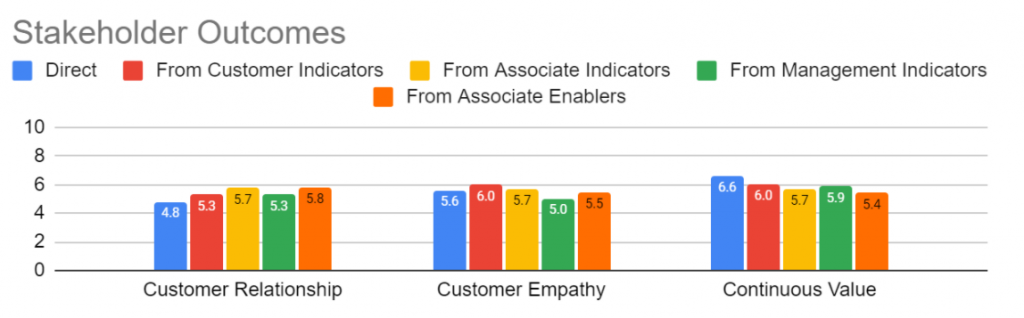
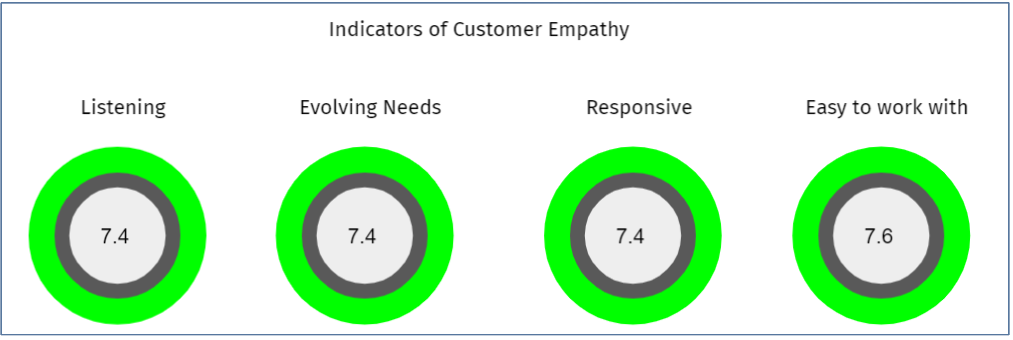
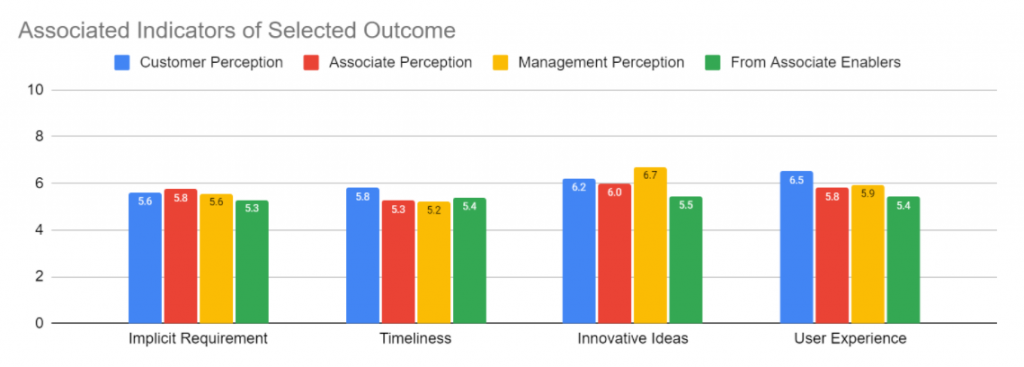
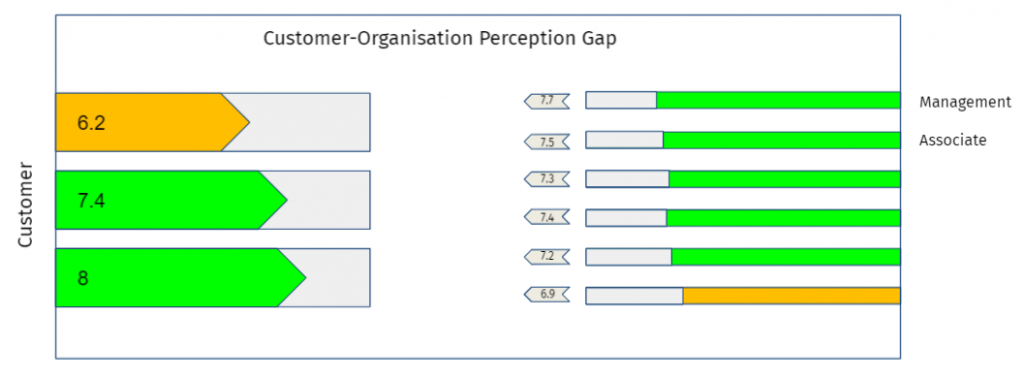
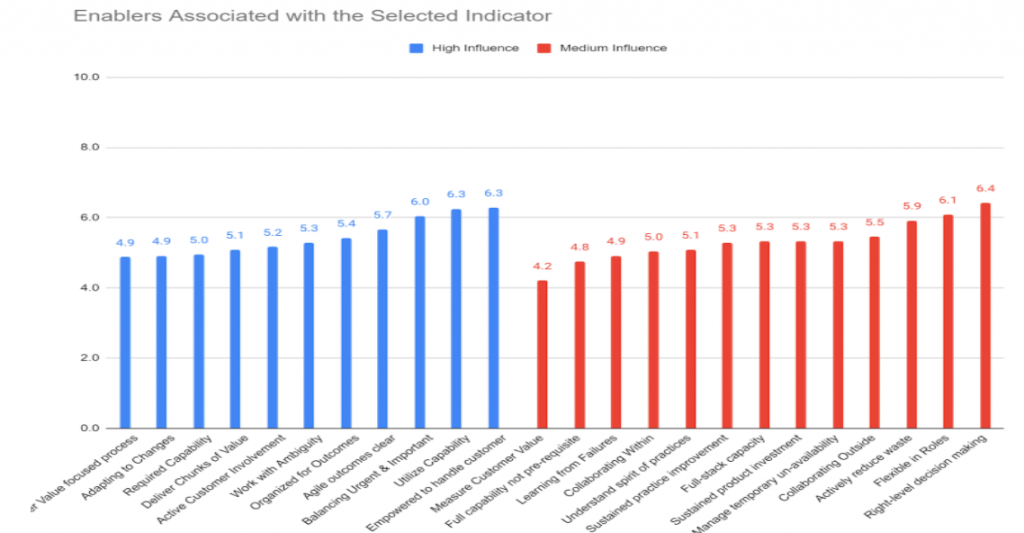
These outputs can be used by organisation management, consultants and coaches to understand what outcomes and indicators need attention. The associated enablers can then be looked at at appropriate actions taken to improve the Agile implementation. This will result in the improvement of the success of the outcomes.

The model mentioned in this article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.





