[Note: ‘ENVISION’ is service marked as a coaching framework by PM Power]
Abstract
This article details out a framework/model that captures PM Power’s principles, techniques, strategies, and methodology for coaching. This framework is called ENVISIONSM, after the coaching methodology adopted. The article first looks at the background our coaching offerings, and the ENVISIONSM framework. It then looks at the principles of coaching adopted by our coaches, the techniques used by them, and the different strategies they use to leverage the different strengths of different coachees. The article then details out the methodology of coaching followed by PM Power coaches. The article concludes by looking at how, and in what circumstances, have our coachees gained from the coaching based on the framework.

Objective
Introduction
PM Power Consulting helps organizations achieve agility in design and delivery of software and services. Founded in 2006, PM Power Consulting is the leader in transformational consulting and coaching, delivered by expert practitioners with decades of experience in building and leading high-performance organizations.
There are three key areas – Project and Program Management; Execution Excellence; and Leadership Development – that PM Power has focused on in its 18 years of delivering consultancy, training, and coaching to a wide range of organizations including large MNCs, Indian enterprises, global in-house centres, software development companies, innovative start-ups as well as non-profit organizations. During this period, we have worked with leaders in our customer organizations and change-agents in the industry world-wide to create, establish, and develop frameworks, values, principles, and practices in these areas. These artefacts have been published and have been used in our consultancy, training and coaching offerings and have proved to be of immense value to our customers and our followers.
PM Power has helped their clients with all three offerings – consulting, training, and coaching.
Consulting is the job of an expert and is problem-solving oriented. The consultant gathers data and analyses the problem, gives expert advice, and recommends solutions for achieving their goals. Over the years, PM Power has executed many consulting assignments. These consulting assignments lead us many a time to our other offerings – training and coaching. Many of our interventions in any selected area have had an element of training initially and a series of coaching interactions with individuals or teams to bring out the best solutions to their current problems. We have also had some training-only or coaching-only interventions.
While training focuses on equipping people with certain required skills by transferring knowledge or skills, coaching is about facilitating and helping people, without prescription, realize their potential and using it achieve their goals. Training is intended for a group. It is structured and curriculum-based, with learning objectives and tests. Coaching on the other hand, is normally personalized (to a person or a team) and non-prescriptive, with an emphasis on asking questions, active listening, and providing support. The idea is to help the individual identify their own solutions and develop their own action plan. The primary goal of coaching is to influence coachee behaviour for the better.
Coaching interventions require a structured approach and tools to get the best out of the process for the coachee. There are many defined frameworks or models that provide this structured approach and tools and are in common use among coaches. Some of them are: The GROW coaching model developed by Graham Alexander, Alan Fine, and Sir John Whitmore; The OSKAR coaching model explained in detail by Mark McKergow and Paul Jackson; The FUEL coaching model outlined John Zenger’s and Kathleen Stinnett’s book; The CLEAR coaching model developed by Peter Hawkings; and The ACHIEVE coaching model by The Coaching Centre (Dembkowski and Eldridge).
PM Power’s proprietary coaching framework/model, ENVISIONSM, is based on inputs and best practices from these different models, and recommendations from the International Coaching Federation and the Coaching Federation of India; and informed and honed by the experience gained in our various interventions and by our coaches’ wide range of experience as individual contributors, managers, and leaders in their previous avatars.
We will now look at the principles, the techniques, strategies and methodology of our coaching that constitutes the framework.
Principles of coaching
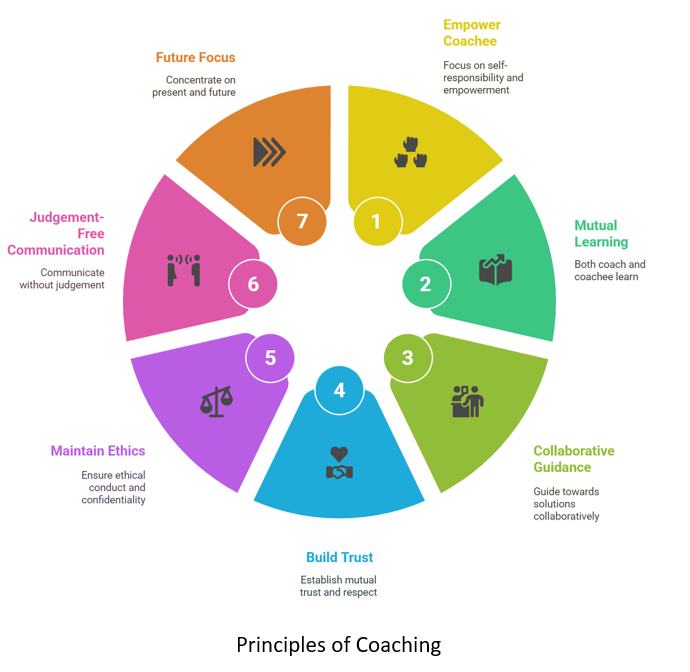
PM Power’s coaching approach is based on the following principles:
- The focus is on the empowerment of the coachee and on their self-responsibility
- The intervention is seen as an opportunity for learning by both coach and coachee
- The coach works on collaboration with the coachee and guiding them towards solutions, not advising them on solutions
- There is mutual trust and respect between the coach and coachee
- Ethical conduct from both sides and confidentiality of the matters discussed
- The coach talks to the coachee without judgement
- The focus is on the present and future, not the past
It is interesting to note that while all our coaches follow the framework and principles noted above, they use a variety of techniques and strategies to help their coachees strengthen themselves. Some of the techniques and strategies used by PM Power coaches are the following.
Coaching techniques
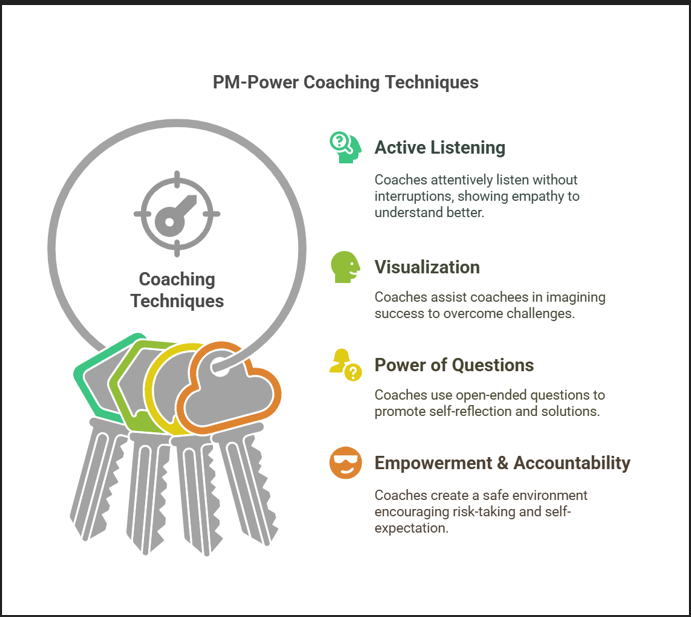
- Active listening: This is a fundamental technique used by the coaches. They all pay attention to what the coachee is saying, avoid interruptions and exhibit empathy with the coachee.
- Visualization: This is a technique used by many of our coaches. It helps the coachee visualize themselves overcoming their issues and limiting beliefs and using their strengths.
- Power of questions: This again is a very critical technique: using open-ended questions and reframing to help with self-reflection and identifying their own solutions, and gain self-awareness and a deeper understanding of themselves.,
- Empowering the coachee and encouraging accountability: This technique helps build a safe environment for the coachee so that they feel secure to take risks and make decisions, and setting expectations for themselves.
Coaching strategies
PM Power stresses on coaching the person rather than the immediate situation or problem. Our coaches use a variety of different strategies and approaches within the framework, based on the particular situation of the coachees. Some of the approaches followed by them are.
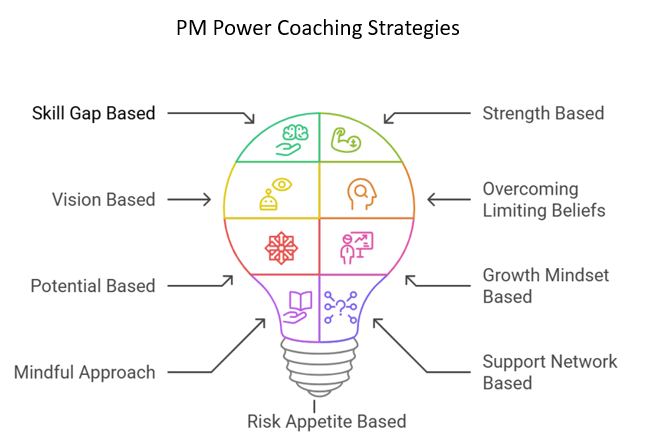
Working on skill gaps: This strategy looks at addressing some skill gap that has been identified by the coachee, and developing those skills. This strategy is also used to help coachees transition to newer or different areas. An example sitaution where this could be used could be where a new manager is struggling with delegation and time management.
- Strength based coaching: This is a very powerful strategy used by some of our coaches with coachees that are demotivated because they feel undervalued and not recognized. It focuses on spotting and identifying the strengths of the coachee and build on it to help themselves achieve their goals. Vision based coaching: This strategy helps the coachee build a vision for themselves and build up their motivations and solutions from this vision. This can be used in a situation where coachee feels the need to progress in their career.
- Overcoming limiting beliefs: Some coaches focus on this and use this strategy over others in situations where the coachee shows diffidence. This helps the coachee come to terms with their limiting beliefs that keep them from achieving their goals. The coach also helps the coachee to develop self-compassion and stop beating themselves up for mistakes.
- Potential based coaching: This is a strategy that can be used with high performing individuals. It tries to identify the coachee’s potential and guide them and develop them towards achieving their vision. This also helps the coachee to achieve higher performance.
- Creating a growth mindset: This strategy is used to help the coachee to adopt a growth mindset to help them face their issues; to always look at experimentation and continuous learning, embrace challenges and proactively seek change, and overcome fear of failure.
- Adopting a mindful approach: This helps coachees who are stressed and anxious to look at their issues and problems without personalising them. This helps them develop awareness of their issue and anxieties, accept them, and look at them impersonally.
- Building a support network: This strategy helps the coachees who feel alone and isolated to find strength to face their issues and problem through building a support system of people who they can trust and who believe in them.
- Risk Appetite: This strategy looks at exploiting the coachee’s risk appetite and their interest in finding new and trailblazing ideas. This is useful in highly innovative environments.
Coaching methodology
Keeping the principles, techniques and strategies of coaching outlined before; taking inputs from the many external models mentioned above; and based on the vast coaching experience of their associates, PM Power has been able to develop a practical coaching methodology. This methodology offers a set of steps that help coaches and coachees work together effectively to achieve desired outcomes.
The names of steps of the methodology make up the acronym ‘ENVISION’. PM Power’s coaching framework which includes their coaching principles, coaching techniques, coaching strategies, and the coaching methodology is called ENVISIONSM after the acronym of the methodology.
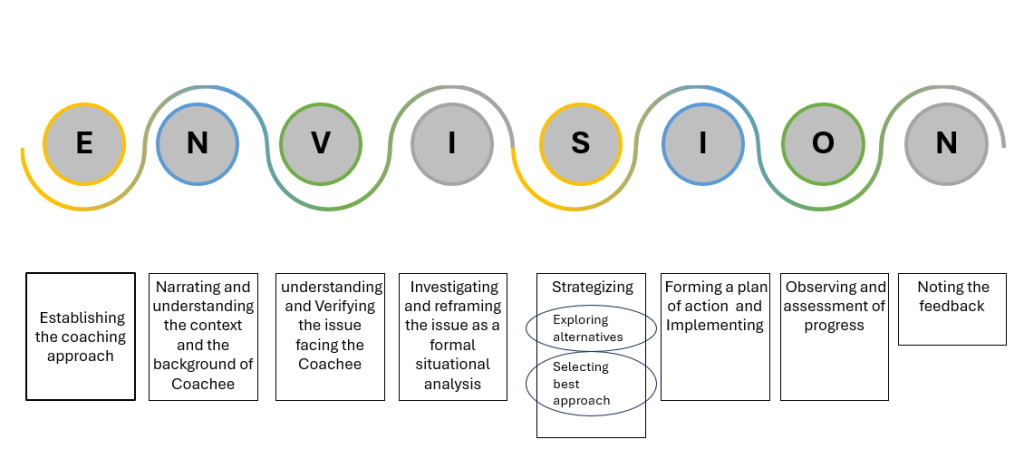
A typical assignment under our coaching methodology goes like this:
- Establishing an environment of trust, confidentiality, and an agreement between coach and coachee,
including clarifying the roles of the coach and coachee, including expectations, boundaries, and commitments; Setting clear, specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound goals for the coaching engagement; and building rapport and trust between the coach and coachee.
- Narrating and understanding the context and the background of the coachee
Background of the local organization of which the coachee is a part and understanding this organization’s place in the bigger organization; Current Situation in the Organization including priorities, challenges and opportunities and financial position; Organizational Dynamics like the culture, how decisions are made and how information is shared; The business situation like the core business, products and services offered, key drivers of revenue and profitability; The organizational hierarchy and structure and where the coachee fits in, and how roles and responsibilities are defined; Growth path of associates looking at career paths, criteria for promotion and advancement, and training and development opportunities; coachee’s background including educational and professional background; their experience; key strengths and weaknesses; their roles and responsibilities and key accomplishments; coachee’s aspirations and vision.
- Understanding and Verifying the issue facing the coachee
Here the coach and the coachee understand and verify the issue that is at the core of the coaching assignment – the main challenge or concern that they are facing right now; for how long; impact of the issue on the coachee’s work; how have they tried to address the issue; and the coachee’s thoughts and feelings about the issue.
- Investigating and creating a formal situational analysis
Here the coachee tries to reframe their issues and concerns as a formal situational analysis: Strengths of the coachee and the organization that can be brought to bear on the issue; the weaknesses that might be the cause of the issue; opportunities to overcome the issue; and the obstacles/threats (internal and external) that the coachee may encounter in trying to solve the issue.
- Strategizing
- Exploring alternatives
In this stage the coachee looks at understanding their strengths, and what are the alternatives to address the issue; working on the weaknesses to improve the situation; using the different opportunities and taking advantage of them to address the issue; alternatives to mitigate the potential obstacles; looking at other creative ways to address the issue; risks and rewards of each approach.
- Selecting the best approach
The coachee selects the best approach (most feasible and realistic, resonating with the coachee and aligning with their vision and goals, best reward/risk ratio) from the alternatives
- Forming a plan of action and Implementing
The coachee forms an action plan to implement the selected approach including specific steps; resources needed; timelines; progress measurement; support needed from coach and others
- Observing and assessment of progress
This stage is set aside for observing and assessing the progress, and planning for the future; including achievement of the goals; impact of and change of perspectives due to the coaching, and changes made; performance improvement; celebrating the success; sustaining the progress; future goals; and ongoing support needed.
- Noting the feedback
This stage is where the coachee can give formal feedback to the coach on the effectiveness of coaching; and effectiveness of the coach-coachee relationship
Conclusion
PM Power has been able to employ this framework in all its coaching assignments. Our coaches have used this framework under many different circumstances and situations like: coaching across different cultures from India and abroad, remote coaching, coaching during stress situations (e.g. pandemic), coaching in organizations which requires high degrees of confidentiality, coaching extremely high-achieving people, and coaching (virtual) teams.
Assignments using the framework have been used to achieve various coachee outcomes like: preparing for a role transition, preparing for a higher position (promotion), performance in challenging business environments, career path decision making, leadership development, professional development, and enhanced and high performance.
Acknowledgements:
- Thanks to JV and ShivK for comments and support in the creation of this article.
- I have used an internal slide deck, called PM Power Coaching Framework, created by Anand, used for selling our coaching offering, for some inputs.
- Thanks to Mohanram, Milind, KP, Vasu, and Ramesh for providing comments and feedback.
- Special thanks to Ramesh for creating the nice colored pictures.
- Thanks to the PM Power coaching task force, consisting of Mohanram, Milind, and KP, for approving the framework and authorizing the publication of it.